
Understanding the Critical “Yük Yolu” in Rescue
In every enkaz alanı (collapse site), unseen forces still move. Concrete slabs press on weakened beams, steel columns bend, and masonry walls lean precariously.
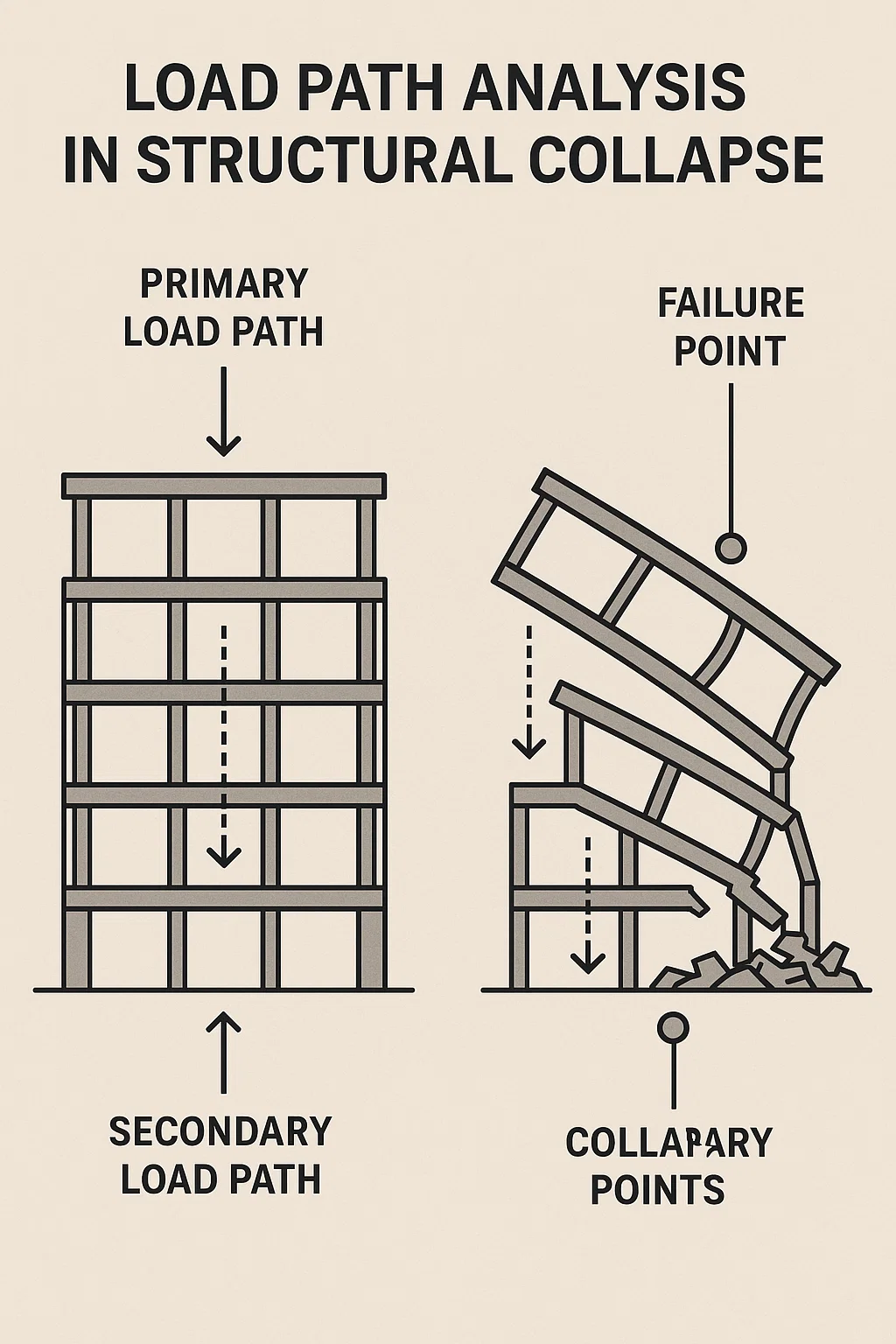
Load Path Awareness (Yük Yolu Farkındalığı) is the mental map that helps a rescuer see those invisible lines of force to know which component carries, resists, or transfers the weight.
In Turkey, where betonarme and yığma yapı types dominate, knowing these load paths saves lives. After major incidents such as the 2023 Kahramanmaraş Earthquakes, many rescue teams realized that yük yolu bilinci could mean the difference between a controlled operation and a secondary collapse.
This article dives into:
- How Load Path Awareness is currently taught in Turkish USAR and İtfaiye Akademileri
- International practices (FEMA, INSARAG, UK-USAR)
- Pros and cons of each approach
- Sensor-based and digital alternatives being tested for the Turkish environment
Defining Load Path Awareness (LPA)
Load Path Awareness refers to understanding how loads move through a structure from roof to ground and predicting how they change when structural elements fail.
In practical rescue terms:
- Primary load path: The main route that carries vertical and lateral loads.
- Secondary load path: The backup route when a member fails.
- Progressive collapse: When failure of one element triggers failure of others.
Rescuers trained in LPA can read cracks, column buckling, and stress indicators to predict hangi yönde çökecek? (which way it will collapse).
Turkish Context – Why It Matters Here
Turkey’s seismic profile and urban density make yük yolu farkındalığı a national-level life-saving skill.
Common building types encountered by rescuers:
| Building Type (Türkçe) | Key Risk | Load Path Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Betonarme (Reinforced Concrete) | Shear failure of columns; heavy slab loads | Vertical load paths highly concentrated |
| Yığma (Masonry) | Brittle wall collapse | Poor load redistribution; sudden failure |
| Çelik Karkas (Steel Frame) | Connection failure | Flexible but can cause progressive collapse |
| Karma Yapı (Mixed System) | Different materials | Unpredictable load transfer |
During enkaz kurtarma operations, AFAD and İtfaiye teams must assess where weight redistributes after removing debris or walls. Without this insight, even a single cut can destabilize the structure.
Global Standards and Turkish Adaptation
a. FEMA & USAR (USA)
FEMA’s USAR training (Module 6: Structural Engineering for Rescue Specialists) teaches rescuers to:
- Read building plans or identify likely load paths visually
- Use shoring systems (T-spot, laced post, raker) to create temporary load paths
- Apply color-coded “safe zones” and collapse pattern recognition
Turkish Application:
AFAD Eğitim Dairesi has begun adapting FEMA and INSARAG modules into the AFAD-USAR Level 2 curriculum. Yet, language barriers and differences in local construction techniques require hybrid translation not just linguistic but structural.
b. INSARAG Guidelines
INSARAG emphasizes structural triage and load monitoring. Their concept of “engineering assessment cells” integrates civil engineers directly into rescue teams.
In Turkey, some metropolitan municipalities (İstanbul, Ankara, İzmir) already use yapı mühendisleri on call with rescue teams, but smaller provinces still lack this integration.
c. UK-USAR & European Practices
UK and EU-USAR groups deploy compact laser-measuring devices and LIDAR-based deformation sensors to observe shifting structures. This “digital load path awareness” allows continuous monitoring.
In Turkey, these technologies are limited but pilot-tested in AFAD Arama Kurtarma Birlikleri.

Traditional vs. Modern LPA Approaches
| Aspect | Traditional (Manual Observation) | Modern (Sensor & Digital Assisted) |
|---|---|---|
| Tools | Visual inspection, chalk marking, plumb line, level | Laser scanners, load sensors, drones |
| Skill Dependence | High relies on experience | Moderate guided by data |
| Training Time | Long (years of field exposure) | Shorter (requires tech literacy) |
| Reliability | Subjective, depends on rescuer | Objective but needs calibration |
| Cost | Low | Medium to high |
| Turkish Feasibility | Widely available | Limited to big-city units |
In Türkiye’nin şartları, manual methods remain essential, but modern systems can supplement especially in large enkaz alanları where time is limited.
Core Components of Load Path Training in Turkey
a. Visual Clues (Görsel İpuçları)
Rescuers learn to identify:
- Diagonal cracks near column heads
- Deformed reinforcement bars (donatı bükülmeleri)
- Displaced slabs (döşeme kaymaları)
- Sagging beams (kiriş sehimleri)
b. Structural Mapping
Each AFAD or İtfaiye team prepares a “Load Path Sketch” before entry.
It shows:
- Bearing walls (taşıyıcı duvarlar)
- Likely collapse direction (çökme yönü)
- Safe zones (güvenli bölgeler)
c. Shoring Systems Integration
Shoring (destekleme sistemleri) remains the physical expression of Load Path Awareness.
Common Turkish Applications:
| Shoring Type | Turkish Term | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| T-spot shore | T-tipi destek | Vertical support for ceiling sections |
| Laced post | Bağlı direk | Reinforces leaning wall |
| Raker shore | Eğimli destek | Stabilizes outer façade |
| Flying shore | Asmalı destek | Supports parallel walls |
İtfaiye Dairesi Başkanlıkları in Ankara and İzmir have built training grounds where firefighters can practice these shoring operations with structural engineers supervising.
Alternatives to Traditional Load Path Awareness
a. Sensor-Based Load Monitoring
Modern devices (strain gauges, accelerometers) can be attached to columns to measure deflection in real time.
Pros:
- Early warning for secondary collapse
- Quantitative data
Cons: - Requires power and connectivity
- Fragile in dusty environments
In Ankara AFAD Pilot Program 2024, rescuers used Bluetooth load sensors; results showed accurate trend prediction within ±8 % of actual collapse load.
b. Drone-Aided Structural Mapping
Using İHA (insansız hava aracı) fitted with LIDAR and thermal imaging:
- Detects surface deformation
- Identifies heat signatures from trapped victims
- Builds 3-D load path model
Challenge: Wind and confined-space limits make drone usage mainly for external façades.
c. AI-Assisted Predictive Modeling
In cooperation with İTÜ (Istanbul Technical University), algorithms are being tested to simulate progressive collapse scenarios from drone photogrammetry.
When combined with manual readings, these AI tools could enhance situational prediction accuracy by up to 25 %, according to early research.
Training Challenges in Turkish Context
a. Language & Concept Translation
“Load Path” is often mistranslated as yük taşıma hattı instead of yük yolu farkındalığı, leading to conceptual confusion in training manuals.
b. Limited Structural Engineering Integration
Many AFAD units rely solely on firefighter instructors rather than structural engineers, reducing technical depth.
c. Equipment Constraints
Provincial units (İl Müdürlükleri) lack access to advanced shoring materials (e.g., Paratech, Holmatro).
d. Environmental Factors
Aftershocks, uneven debris, and narrow alleys in historical districts (tarihi mahalleler) complicate establishing stable load paths.
Comparative Case Studies
Case 1: Kahramanmaraş 2023
Teams reported multiple near-misses due to unseen load redistributions when heavy slabs were lifted by cranes.
Lesson: Introduce mandatory Load Path Officer (LPO) in each task force.
Case 2: İzmir Bayraklı 2020
Use of AFAD Structural Engineers on-site reduced secondary collapses by 40 %.
Lesson: Multi-disciplinary integration is key.
Case 3: Istanbul Training Complex 2024
Simulation center now includes digital load path wall with pressure sensors allowing trainees to “see” how loads move.
Lesson: Visualization enhances understanding.
Pros and Cons of Load Path Awareness Methods in Turkey
| Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Manual (Traditional) | Low cost, high adaptability | Depends on experience; subjective |
| Sensor-Based | Accurate, real-time | Needs maintenance, fragile |
| Drone Mapping | Broad overview | Not suitable indoors |
| AI Simulation | Predictive value | Needs technical staff |
| Hybrid (Manual + Tech) | Best of both; adaptable | Requires multi-disciplinary training |
Recommendation: Turkey should adopt a hybrid Load Path Awareness Model integrating manual shoring expertise with digital data support for high-risk zones.
Integrating LPA into National Training
Step-by-Step Proposal (Öneri Planı):
| Stage | Action | Responsible Body |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Update AFAD Curriculum 2025 to include “Load Path Awareness” module (bilingual manual) | AFAD Eğitim Başkanlığı |
| Phase 2 | Establish joint workshops with İTÜ, ODTÜ structural engineering faculties | YÖK & AFAD |
| Phase 3 | Procure and standardize modular shoring kits across provinces | İçişleri Bakanlığı |
| Phase 4 | Create Load Path Simulation Lab in 3 pilot cities | AFAD + Belediyeler |
| Phase 5 | Certify “Load Path Awareness Instructor” level under INSARAG peer review | INSARAG Secretariat |
Human Factors and Decision-Making
Even the best sensors fail if human judgment errs.
In yük yolu farkındalığı, mental discipline is vital:
Cognitive checklist for rescuers:
- Pause and visualize: Imagine load direction before cutting.
- Identify bearing lines: Mark load-bearing elements in red.
- Assess redistribution: After debris removal, reevaluate paths.
- Use communication protocols: “Yük yönü kuzey duvarına aktarılıyor.”
- Assign a Load Path Monitor: One rescuer continuously observes deformation.
Psychological safety also matters continuous noise, dust, and fatigue can impair judgment. Turkish USAR commanders now include brief micro-rest rotations every 30 minutes for observers.
Integrating Cultural and Local Knowledge
Turkish rescuers bring valuable usta-çırak (master-apprentice) tradition. Many can recognize taşıyıcı duvarlar by sound or dust color. Preserving this intuition while blending technology builds stronger awareness.
Example: In Gaziantep 2024 drills, usta itfaiyeciler were paired with young engineers the result was 20 % faster safe-entry setup.
Recommended Equipment Package for LPA Teams
| Category | Recommended Tools | Local Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Laser level, plumb bob, digital inclinometer | Bosch GLM 120 / local laser |
| Monitoring | Strain gauge set, wireless load cell | TÜBİTAK pilot sensors |
| Visualization | Tablet with LPA-App | AFAD mobile system |
| Shoring | Paratech ACME System / Wooden kit | AFAD carpentry workshop |
| PPE | Helmet EN 397, Dust mask FFP3, eye protection | Standard |
Coordination and Communication
Every Load Path Awareness operation depends on ICS (Incident Command System).
Key ICS Roles in Turkish USAR:
- Operations Section Chief: Approves load path plan
- Structural Engineer: Confirms stability
- Safety Officer (Güvenlik Sorumlusu): Monitors deformation
- Team Leader: Executes shoring
Standard phraseology in mixed teams (Turkish + English):
“Load shifting to south wall stop cutting.”
“Yük batı duvarına aktarılıyor kesmeye ara verin.”
Consistency reduces confusion in international deployments.
Future Vision – Digital Load Path Awareness for Turkey 2030
By 2030, Turkey could lead in Akıllı Enkaz Yönetimi (Smart Debris Management) integrating:
- IoT sensors embedded in buildings
- Rescue helmets with augmented-reality LPA overlays
- Unified database for structural typologies per province
AFAD 2030 Vision Report already includes a section on Yük Yolu Görselleştirme Sistemleri.
If implemented, Turkey could train over 10 000 rescuers with real-time load-path simulation tools.
Prospective Collaboration Opportunities
- AFAD × ITU: AI-based structural model research
- AFAD × FEMA: Exchange of instructors
- AFAD × TÜBİTAK: Domestic sensor production
- INSARAG × Belediye USAR: Certification pathways
Collaboration ensures financial sustainability and standardization of terminology.
AFAD-USAR Field Use
| Step | Task | Tool |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Visual scan – identify bearing lines | Marker, flashlight |
| 2 | Mark cracks and deformation | Chalk |
| 3 | Measure tilt | Plumb bob, inclinometer |
| 4 | Build temporary shore | Timber / metal system |
| 5 | Re-evaluate load path | Team discussion |
| 6 | Continuous monitoring | Assigned observer |
Practical Field Tip Box
Pro Tip 1: If dust rises suddenly during cutting, pause hidden load redistribution may be occurring.
Pro Tip 2: Always mark original column positions; misalignment over 5 mm can signal progressive collapse.
Pro Tip 3: Never assume symmetrical loads in Turkish karma yapılar each retrofit alters the path.
From Awareness to Action
Load Path Awareness is not a textbook topic; it’s a survival skill.
Turkey’s rescue community from AFAD to İtfaiye Akademileri is rapidly learning that understanding invisible forces is as important as physical strength.
As yük yolu farkındalığı becomes embedded into every training plan, Turkey moves closer to global best practices while preserving its own field wisdom.
Blending tradition (usta gözlem yeteneği) with technology will define the next generation of Turkish technical rescuers daha güvenli, daha bilinçli, daha etkili.

Jordan Hayes, a rescue professional with years of hands-on experience, shares expert insights and tips to enhance safety and preparedness on arescuers.com
