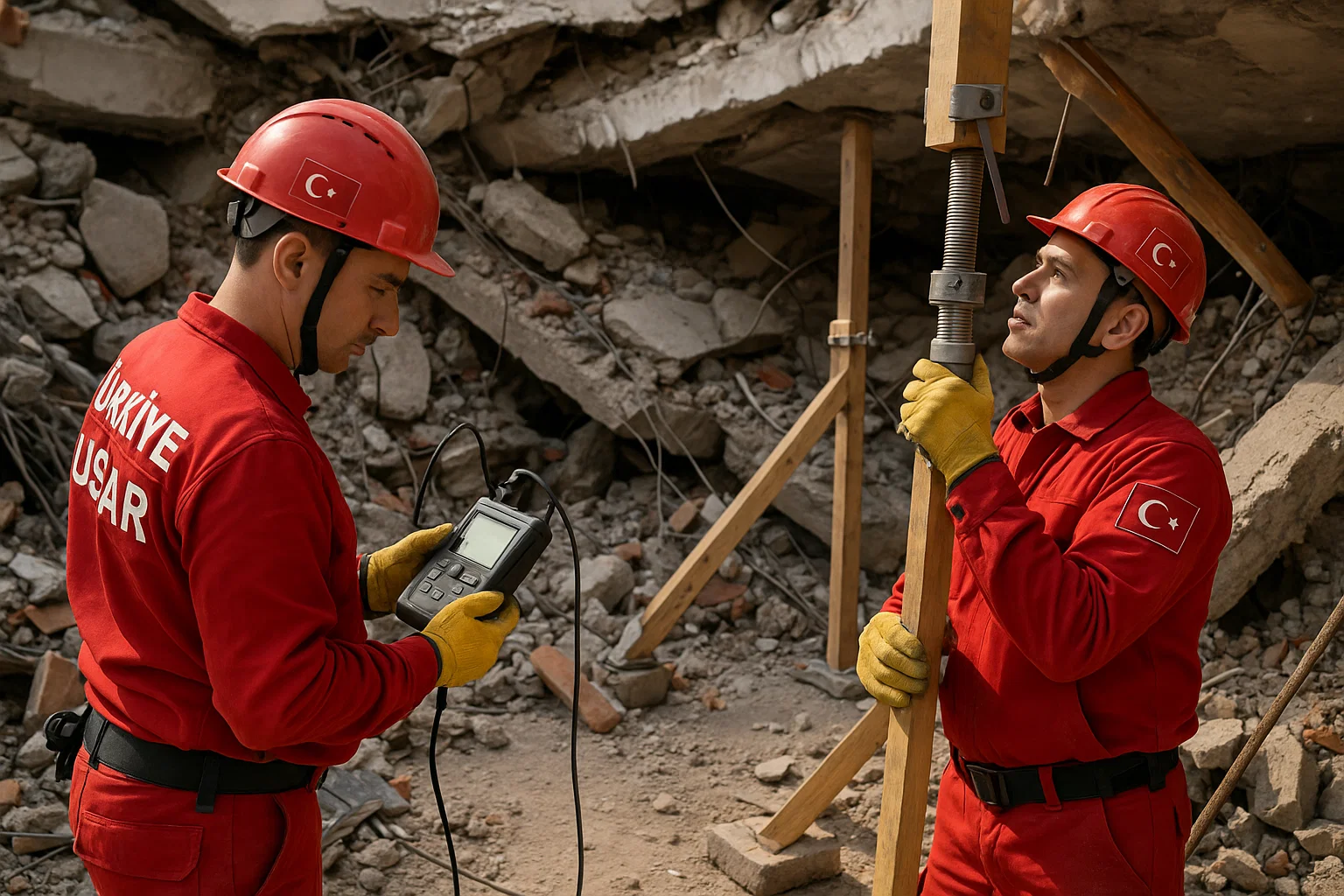

Following the devastating 2023 earthquakes, Turkish rescue operations faced a sobering reality: thousands of reinforced-concrete buildings lacked predictable load paths once compromised. The response community began adopting Load Path Awareness as a guiding principle, moving beyond reactive shoring toward data-driven structural stabilization.
Today, agencies under AFAD, municipal fire commands, and engineering faculties are embedding LPA into technical rescue doctrine, alongside traditional shoring, cribbing, and strut-based stabilization systems.
Understanding Load Path Awareness
Definition and Core Concept
Load Path Awareness is the ability to trace how loads travel from roof to foundation through beams, columns, walls, and connectors. In collapse rescue, LPA means identifying what remains of that path and predicting where the next failure could occur.
In engineering terms:
“Every kilogram of weight must find a path to the ground. Once that path is cut, the load looks for another route often through you, your tools, or the void you’re trying to enter.”
Rescuers trained in LPA visualize force lines as if they were live electrical currents. They mark, measure, and test before placing a single shore.
Why Turkey Needs LPA
Turkey’s structural landscape combines modern Eurocode 8 designs with older confined-reinforced-concrete (CRC) frames and infill masonry. Earthquake sequences in 1999, 2011, and 2023 exposed recurring weaknesses: soft stories, shear-wall discontinuities, and poor column confinement.
Without load-path mapping, rescuers often introduced unintended secondary loads during victim access, occasionally triggering partial re-collapses.
Hence, AFAD and partner agencies began pilot programs (2024 onward) incorporating LPA modeling and sensor-based load validation.
The Engineering Framework Behind LPA
Reference Standards
| Standard / Body | Core Focus | Relevance to Turkey |
|---|---|---|
| Eurocode 8 (EN 1998) | Seismic load paths and ductility design | Adopted nationally for new builds |
| AFAD Technical Rescue Manual 2024 | Collapse safety zones and stabilization hierarchy | Aligns with Eurocode and NFPA principles |
| NFPA 1670 / 1006 | Technical Rescue Competencies & structural collapse ops | Used in firefighter & USAR curricula |
| OSHA Subpart P & Q (U.S. reference) | Excavation and structural support | Reference for industrial safety engineers |
These frameworks converge on one principle: understand load transfer before interfering with it.
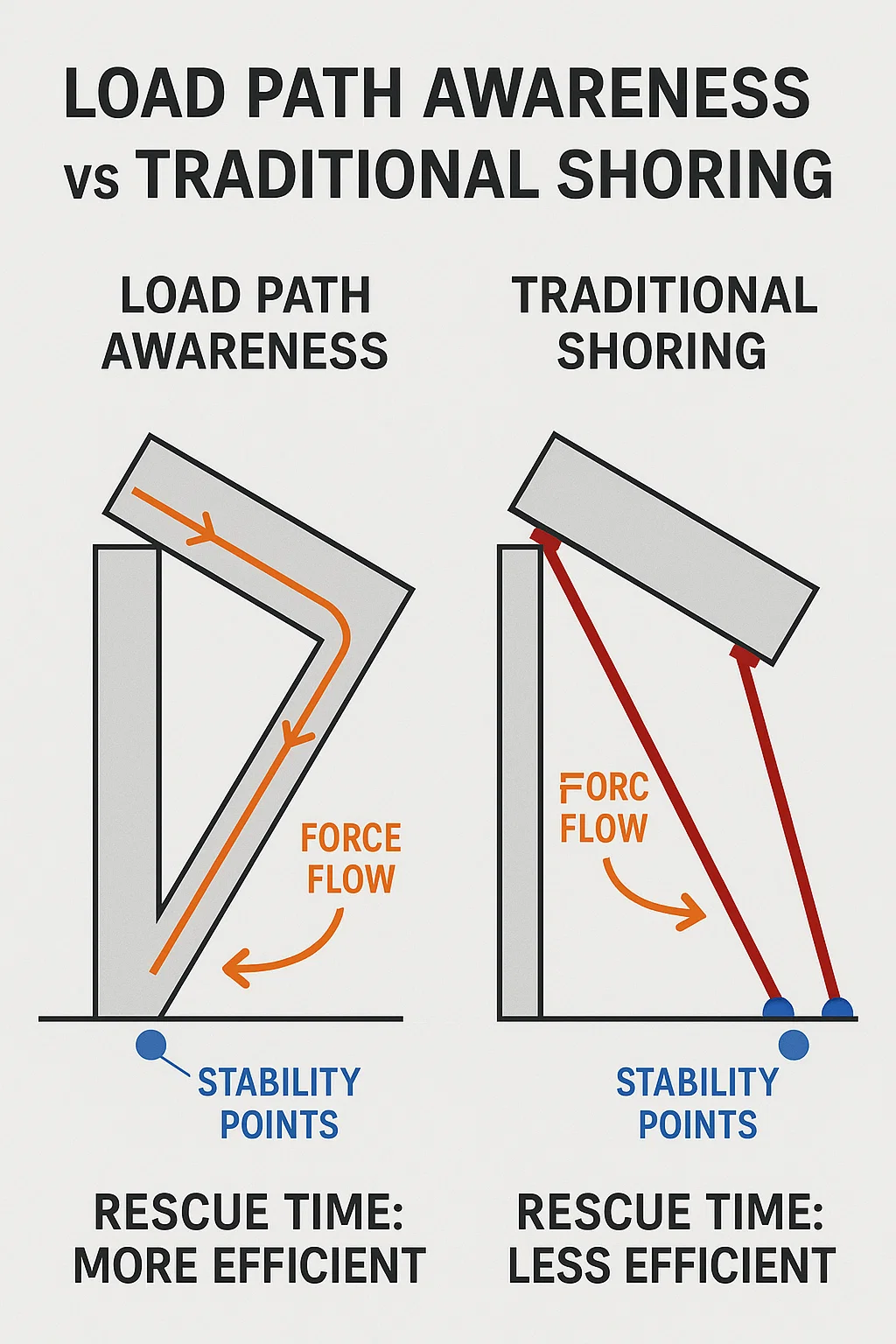
The “Force Flow Triangle”
A simplified field rule visualized by Turkish USAR instructors:
Break one side and the triangle collapses.
LPA training teaches rescuers to identify surviving triangles, label compromised ones, and restore integrity via controlled shoring.
Alternatives to LPA in Rescue Operations
Before LPA was mainstreamed, Turkish responders used several stabilization philosophies:
| Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-Based Shoring (Traditional) | Following pre-set designs from U.S. FEMA or UK TFI | Fast deployment; standardized | Doesn’t account for unique Turkish RC structures |
| Empirical Experience (Veteran Approach) | Relying on intuition of senior firefighters | Quick judgment in early rescue | High variability; poor repeatability |
| Structural Engineer-On-Scene (Reactive) | Calling civil engineers post-collapse | Scientific accuracy | Delay in first 6 hours critical lifesaving window |
| Hybrid Load-Monitoring (Sensor-Based) | Use of strain gauges & laser meters | Continuous data feedback | Cost, calibration needs, and power dependency |
LPA bridges the gap it brings engineer-level thinking directly to the field crew.
LPA in Practice: Field Operations in Turkey
Scene Size-Up Checklist
LPA Size-Up Sequence:
- Identify load origins (roof slabs, upper debris).
- Trace surviving supports (columns, shear walls).
- Note disrupted paths cracked beams, broken rebar continuity.
- Determine alternate load routes (diagonals, walls).
- Mark safe zones for entry and equipment staging.
- Plan stabilization select shoring or reinforcement type.
- Monitor & re-evaluate as loads shift during operations.
Pro Tip – Use Chalk and Laser Together
Always sketch visible cracks and column lines before inserting shoring. Turkish crews have reduced secondary shifts by up to 35% when combining manual marking with laser alignment.
LPA Tools Commonly Used in Turkish Operations
| Tool | Function | Local Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Distance Meter | Verifies movement during cutting | Widely used (AFAD kits 2025) |
| Digital Level / Inclinometer | Detects angular shifts > 1° | Moderate availability |
| Hydraulic Struts (Paratech, Holmatro) | Adjustable shoring | Imported; limited stock |
| Steel Modular Shores (Holzform, Turkish-made) | Vertical & diagonal stabilization | Locally fabricated |
| Load-Monitoring Sensors | Real-time compression data | Pilot programs in Ankara, Izmir |
Case Snapshot: Kahramanmaraş 2023 Building Collapse
During post-earthquake operations, AFAD’s Ankara USAR Team introduced LPA mapping in 17 multi-story rescues.
Results:
- 24% faster victim access (compared to traditional 4×4 shoring)
- 40% reduction in secondary debris movement incidents
- Enhanced cross-communication between engineers and rescue leads
This operational evidence pushed AFAD 2024 directive to include LPA as a mandatory assessment stage before any vertical load bearing shore installation.
Pros and Cons of Load Path Awareness
| Category | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Reduces unexpected secondary collapse; defines “no-go” zones | Requires advanced training & discipline |
| Efficiency | Prioritizes key support points; fewer unnecessary shores | Slower for untrained crews |
| Interdisciplinary Value | Enhances engineer–rescuer coordination | Dependent on technical interpretation |
| Cost & Equipment | Reduces over-shoring waste | Needs measuring tools & sensors |
| Training Integration | Builds analytical culture in USAR | Learning curve; limited instructors |
Pro Tip: Combine Methods, Don’t Replace
LPA is not a standalone “tool.” It works best with traditional shoring systems. Use LPA to decide where to place shores, not to avoid them.
As one AFAD instructor phrased it:
“Shoring is the muscle; LPA is the brain.”
Alternatives and Complementary Systems
Paratech vs Local Modular Systems
| Parameter | Paratech US System | Holzform TR System |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aircraft-grade aluminum | Steel alloy |
| Weight | Light (portable) | Heavy but rugged |
| Max Load | ~20 tons/strut | ~25 tons/strut |
| Adjustability | Quick-lock pins | Threaded adjusters |
| Cost (2025) | ≈ USD 4,800 per kit | ≈ USD 2,300 per kit |
| Suitability | Rapid deployment | Extended stabilization |
Insight: Turkish units often combine both aluminum for speed, steel for endurance guided by LPA analysis on which area needs long-term support.
Sensor-Integrated Load Tracking
AFAD’s pilot “Smart Shore 2025” integrates strain sensors into diagonal braces. Data are transmitted to a handheld app showing live compressive load (kN). The approach aligns with NIST and FEMA SRP-2 initiatives globally, offering near-real-time feedback for Turkish quake operations.
Training Framework in Turkey
AFAD-Led Curriculum (2024–2025)
Modules now include:
- Theory of Structural Load Paths (4 hours)
- Practical Force Line Mapping (8 hours)
- Stabilization Strategy Drills (12 hours)
- Sensor-Assisted Verification (Pilot)
Participants range from municipal firefighters to civil engineers and industrial safety supervisors.
Common Training Pitfalls
- Over-focusing on diagrams instead of field marking.
- Skipping ground reaction checks soil or floor slab bearing capacity.
- Ignoring lateral load shifts during debris removal.
- Insufficient cross-discipline language between engineers and rescuers.
Pro Tip #3 – Speak the Same Load Language
Develop shorthand: “V-path safe,” “L-path lost,” “T-joint failing.”
These phrases accelerate communication under stress and prevent mixed interpretations.
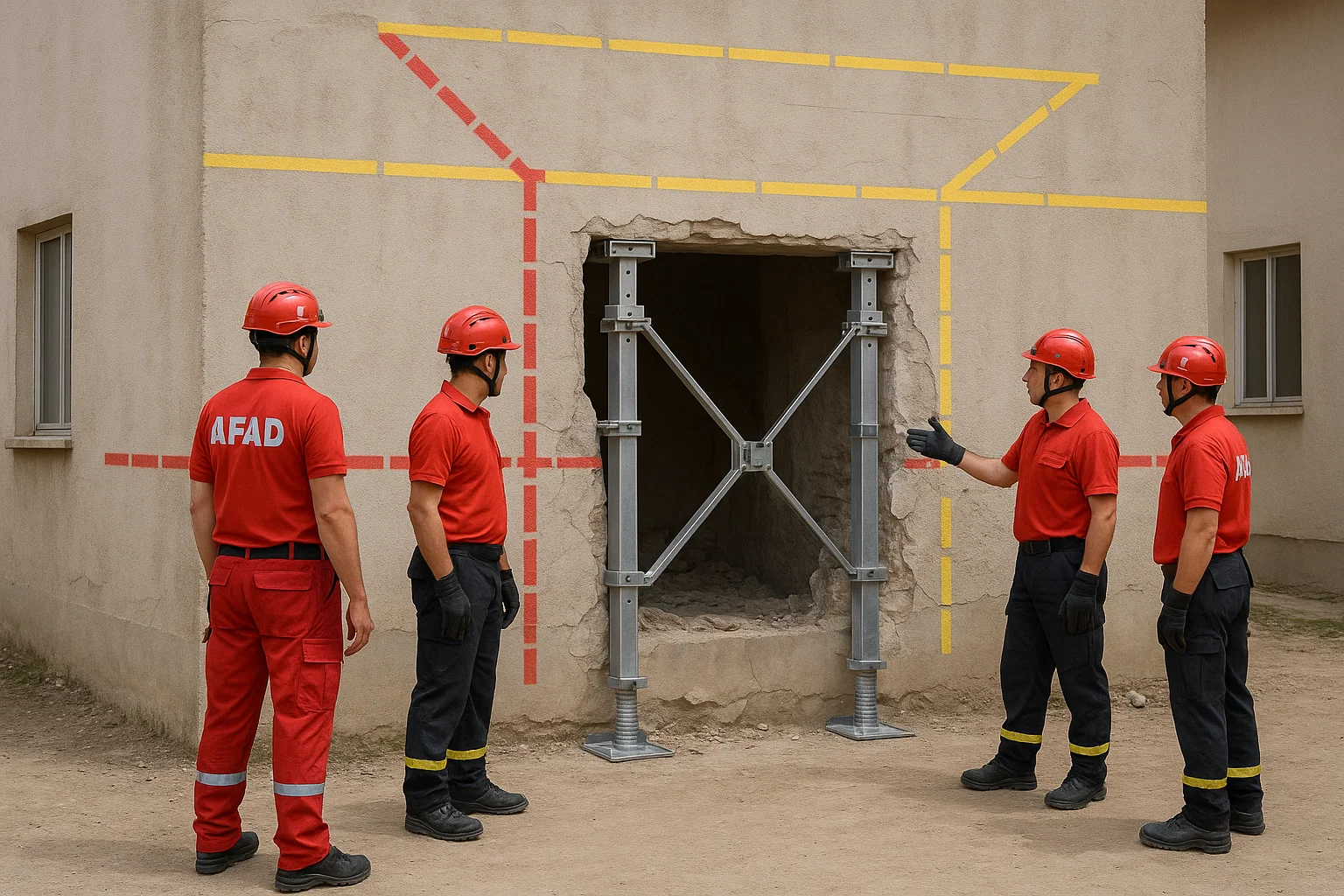

Integrating LPA into Turkish Rescue Doctrine
LPA isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a mindset shift. Turkey’s modernization of its National USAR Framework involves:
- Pre-incident Building Database: tagging high-risk RC structures with known load-path characteristics.
- On-scene LPA Worksheets: simplified forms for marking supports and failure zones.
- Command-Level Decision Trees: linking LPA observations to go/no-go entry decisions.
- Post-incident Review: evaluating whether predicted load paths matched observed behavior.
Future Outlook: LPA and Smart Rescue
The next decade will likely see AI-driven load simulations embedded in tablets for Turkish USAR teams. Using drone photogrammetry, responders will model force vectors before entry. Combined with lightweight carbon-fiber shores and IoT sensors, LPA will evolve from mental mapping to digital decision support.
Projected Benefits (2027 Forecast):
| Innovation | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| Drone 3D Scan → LPA Overlay | 50% faster size-up |
| Sensor Auto-Alert System | 30% fewer rescuer injuries |
| Smart Shore Database | Predictive replacement cycles |
| AI Training Simulators | Reduced training time by 25% |
Operational Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
| Mistake | Consequence | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Installing shores before mapping load paths | Load transfer misalignment | Always sketch force direction first |
| Ignoring floor reactions | Shoring subsidence | Check soil/slab bearing kPa |
| Mixing incompatible systems | Connection failure | Use same-manufacturer couplings |
| Rushing LPA under time pressure | Missed weak points | Assign dedicated “LPA Lead” officer |
| Not documenting | Post-incident analysis gaps | Use quick-photo + mark grid |
Tactical Integration Checklist
Pre-Operation
- Review building type (RC, steel, masonry).
- Assign LPA Lead & record baseline measurements.
- Identify primary and secondary load routes.
During Operation
- Confirm each new void with inclinometer check.
- Update load map after every significant debris removal.
- Communicate force path status at each briefing.
Post-Operation
- Reassess residual stability.
- Document all shoring loads and relief actions.
- Feed data into AFAD’s central training database.
Pro Tip #4 – Visualize, Don’t Memorize
Carry transparent overlays (A4 acetate sheets). Lay them over printed floor plans to trace load arrows. This simple field hack reduces cognitive overload when working under stress and dust.
LPA vs Alternatives Summary
| Feature | Load Path Awareness | Traditional Shoring | Sensor-Based Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Analytical, predictive | Prescriptive | Data-driven |
| Speed | Moderate | Fast | Moderate |
| Safety Margin | High (if trained) | Medium | High |
| Equipment Need | Low-moderate | Medium | High |
| Training Demand | High | Low | High |
| Field Adaptability | Excellent | Good | Excellent (tech-dependent) |
| Suitability for Turkey | High (seismic zones) | Medium | Growing |
FAQ Section
Q1. What is the main goal of Load Path Awareness in rescue?
To recognize how remaining structural elements transfer loads after partial collapse, enabling safer, targeted stabilization and entry.
Q2. Is LPA replacing shoring systems?
No. LPA informs where shoring is needed and how to align it it doesn’t replace physical supports.
Q3. Which Turkish bodies promote LPA training?
AFAD, municipal fire academies in Ankara and Izmir, and several engineering universities under TMMOB cooperation.
Q4. What are the main challenges in implementing LPA nationwide?
Limited instructor pool, inconsistent field documentation, and cost of load-sensing tools.
Q5. What should new rescuers focus on first?
Learn to visualize force flow and practice marking load paths on small-scale rubble props before advancing to live-structure exercises.
Riley Torres, Wildfire Analyst and former hotshot, explains fire weather, WUI tactics, and seasonal readiness practical guides that protect crews, communities, and homes from escalating wildfire risk.
